Python沙箱逃逸
执行模块
在Python中执行系统命令的方式有
- os
- commands:仅限
2.x - subprocess:subprocess.getoutput(“whoami”),print(a);subprocess.run(“whoami”)
- timeit:timeit.sys,
timeit.timeit("__import__('os').system('whoami')", number=1) - platform:platform.os,platform.sys,platform.popen(‘whoami’, mode=’r’, bufsize=-1).read()
- pty:pty.spawn(‘ls’),pty.os
- bdb:bdb.os,cgi.sys
- cgi:cgi.os,cgi.sys
- ….
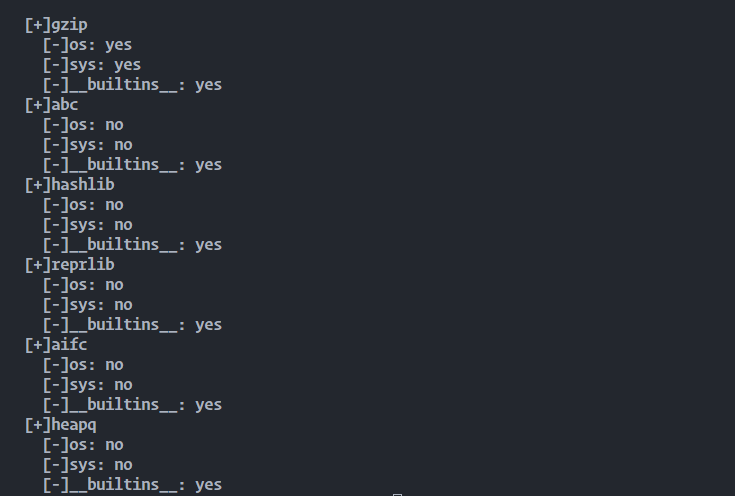
下面是一个脚本,跑出了其中导入os或者sys还有__builtins__的库:
1 | |
效果是这样:
禁止import os
1 | |
如果禁用了import os,可以使用空格绕过,如果空格被过滤,可以尝试__import__:__import__('os'),__import__被禁了还有 importlib(Python3.x),imp(Python2.x),execfile()(Python2.x)等等
最后两种方法都需要库的路径一般情况下都是默认的,还有方法找路径的话就是用
1 | |
关键字过滤
代码中要是出现 os,直接不让运行。那么可以利用字符串的各种变化来引入 os:
1 | |
1 | |
1 | |
还可以利用 eval 或者 exec:
1 | |
对于绕过操作还有很多比如说:逆序、变量拼接、base64、hex、rot13等等
sys.modules
sys.modules 是一个字典,里面储存了加载过的模块信息。如果 Python 是刚启动的话,所列出的模块就是解释器在启动时自动加载的模块。有些库例如 os 是默认被加载进来的,但是不能直接使用,原因在于 sys.modules 中未经 import 加载的模块对当前空间是不可见的。
如果将 os 从 sys.modules 中剔除或者改变,os 就彻底没法用了:
1 | |
假如遇到上面这种让os模块成了字符串,绕过思路就是将其删除掉,重新加载
1 | |
执行函数
通过上面内容我们很容易发现,光引入 os 只不过是第一步,如果把 system 这个函数干掉,也没法通过os.system执行系统命令,并且这里的system也不是字符串,也没法直接做编码等等操作。
不过,要明确的是,os 中能够执行系统命令的函数有很多:
1 | |
应该还有一些,可以在这里找找:
- Python2.x :https://docs.python.org/2/library/os.html
- Python3.x :https://docs.python.org/3/library/os.html
其次,可以通过 getattr拿到对象的方法、属性:
1 | |
与 getattr 相似的还有 __getattr__、__getattribute__,它们自己的区别就是getattr相当于class.attr,都是获取类属性/方法的一种方式,在获取的时候会触发__getattribute__,如果__getattribute__找不到,则触发__getattr__,还找不到则报错。
__builtin__,builtins与__builtins__
在python2.x的版本中,内置模块被命名为了__builtin__,到了python3.x就成了builtins都需要将其导入才能查看:
2.x:
1 | |
3.x:
1 | |
__builtins__实际就是__builtin__,builtins的引用,它不需要导入即可使用,但是__builtins__与__builtin__和builtins还是有一个小区别,就是在局部的作用域中(一个函数内部,比如说 print(eval(inp, {"__builtins__": None, 'f': f, 'eval': ev4l})))__builtins__ 就是是一个字典类似于__builtin__.__dict__的引用,而非__builtin__本身。还有我觉得有必要了解下Python 对函数、变量、类等等的查找方式是按 LEGB 规则来找的。
那什么是LEGB呢?
- L(Local)——局部作用域
- 当前函数或代码块内部定义的变量。
- 如果在函数内定义了一个变量,Python 首先会在当前函数的局部作用域内查找。
- E(Enclosing)——闭包函数外的局部作用域
- 如果局部作用域中没有找到变量,Python 会查找外层函数(即闭包)中定义的变量。
- 适用于嵌套函数的场景,即函数内部定义了另一个函数。
- G(Global)——全局作用域
- 如果在局部和闭包作用域中都找不到变量,Python 会查找模块的全局作用域。
- 全局作用域中的变量通常定义在脚本的顶层,或者是
global声明的变量。
- B(Built-in)——内置作用域
- 如果上述作用域都找不到变量,Python 会在内置作用域中查找。
- 内置作用域包含 Python 语言提供的内置函数和变量,例如
len()、print()和Exception。
查找顺序:
Python 遇到变量时会按照 L → E → G → B 的顺序依次查找,直到找到匹配的变量为止。如果所有作用域都找不到,会抛出 NameError。
回归话题__builtins__有很多有意思的函数
1 | |
如果遇到将__builtins__里面的危险函数删除又该如何绕过嘞?
1 | |
可以利用 reload(__builtins__) 来恢复 __builtins__。但是,我们在使用 reload 的时候也没导入,说明reload也在 __builtins__里,那如果连reload都从__builtins__中删了,就没法恢复__builtins__了,需要另寻他法。
注意:2.x 的 reload 是内建的,3.x 需要 import imp,然后再 imp.reload
继承关系绕过
1 | |
其中__mro__,是个元组,记录了继承关系:
1 | |
类的实例在获取 __class__ 属性时会指向该实例对应的类。可以看到,''属于 str类,它继承了 object 类,这个类是所有类的超类。具有相同功能的还有__base__和__bases__。需要注意的是,经典类需要指明继承 object 才会继承它,否则是不会继承的:
由于:没法直接引入 os,那么假如有个库叫A,在A中引入了os,那么我们就可以通过__globals__拿到 os(__globals__是函数所在的全局命名空间中所定义的全局变量)。例如,site 这个库就有 os:
1 | |
也就是说,能引入 site 的话,就相当于有 os。那如果 site 也被禁用了呢?没事,本来也就没打算直接 import site。可以利用 reload,变相加载 os:
1 | |
所有类都继承object,那么看看他的子类(Python2.x),(Python3.x,for i in enumerate(''.__class__.__mro__[-1].__subclasses__()): print(i)):
1 | |
可以看到,site 就在里面,以 2.x 的site._Printer为例:
1 | |
os 又回来了。并且 site 中还有 __builtins__。
这个方法不仅限于 A->os,还阔以是 A->B->os,比如 2.x 中的 warnings:
1 | |
其中warnings这个库中有个函数:warnings.catch_warnings,它有个_module属性:
1 | |
所以通过_module也可以构造 payload:
1 | |
3.x 中的warnings虽然没有 linecache,也有__builtins__。
1 | |
如果object没被过滤还可以这样
1 | |
还有一种是利用builtin_function_or_method 的 __call__:
1 | |
还有
1 | |
还有
1 | |
上面的这些利用方式总结起来就是通过__class__、__mro__、__subclasses__、__bases__等等属性/方法去获取 object,再根据__globals__找引入的__builtins__或者eval等等能够直接被利用的库,或者找到builtin_function_or_method类/类型__call__后直接运行eval。
文件读写
2.x 有个内建的 file:
1 | |
还有个 open,2.x 与 3.x 通用。
还有一些库,例如:types.FileType(rw)、platform.popen(rw)、linecache.getlines(r)。
为什么说写比读危害大呢?因为如果能写,可以将类似的文件保存为math.py,然后 import 进来: math.py:
1 | |
调用
1 | |
这里需要注意的是,这里 py 文件命名是有技巧的。之所以要挑一个常用的标准库是因为过滤库名可能采用的是白名单。并且之前说过有些库是在sys.modules中有的,这些库无法这样利用,会直接从sys.modules中加入,比如re:
1 | |
当然在import re 之前del sys.modules['re']也不是不可以…
最后,这里的文件命名需要注意的地方和最开始的那个遍历测试的文件一样:由于待测试的库中有个叫 test的,如果把遍历测试的文件也命名为 test,会导致那个文件运行 2 次,因为自己 import 了自己。
读文件暂时没什么发现特别的地方。
剩下的就是根据上面的执行系统命令采用的绕过方法去寻找 payload 了,比如:
1 | |
过滤了[]
用pop、__getitem__ 代替(实际上a[0]就是在内部调用了a.__getitem__(0))
1 | |
CTF题目
来自iscc 2016的Pwn300 pycalc
1 | |
exec command in _global这一句就把很多 payload 干掉了,由于 exec 运行在自定义的全局命名空间里,这时候会处于restricted execution mode
1 | |
不过也正是由于 exec 运行在特定的命名空间里,可以通过其他命名空间里的 __builtins__,比如 types,json 库,来执行任意命令:
1 | |
两个payload本质区别在取导入的时不同的库